Bronchoscopy & blood gas analysis
Diagnosis of horses with lung disease
Diagnosis of horses with lung disease
If the horse suddenly starts coughing, good advice is hard to come by. The vet is the best person to contact to get to the bottom of respiratory problems. But what if auscultation, blood tests and medication do not bring any improvement? Then bigger guns have to be brought out: Further diagnostics help to find the cause of respiratory problems and can be an important piece of the puzzle in the horse's recovery.
The most common further diagnostic measures in horses include bronchoscopy and blood gas analysis, as well as the cytological evaluation of respiratory smears.
The most common further diagnostic measures in horses include bronchoscopy and blood gas analysis, as well as the cytological evaluation of respiratory smears.
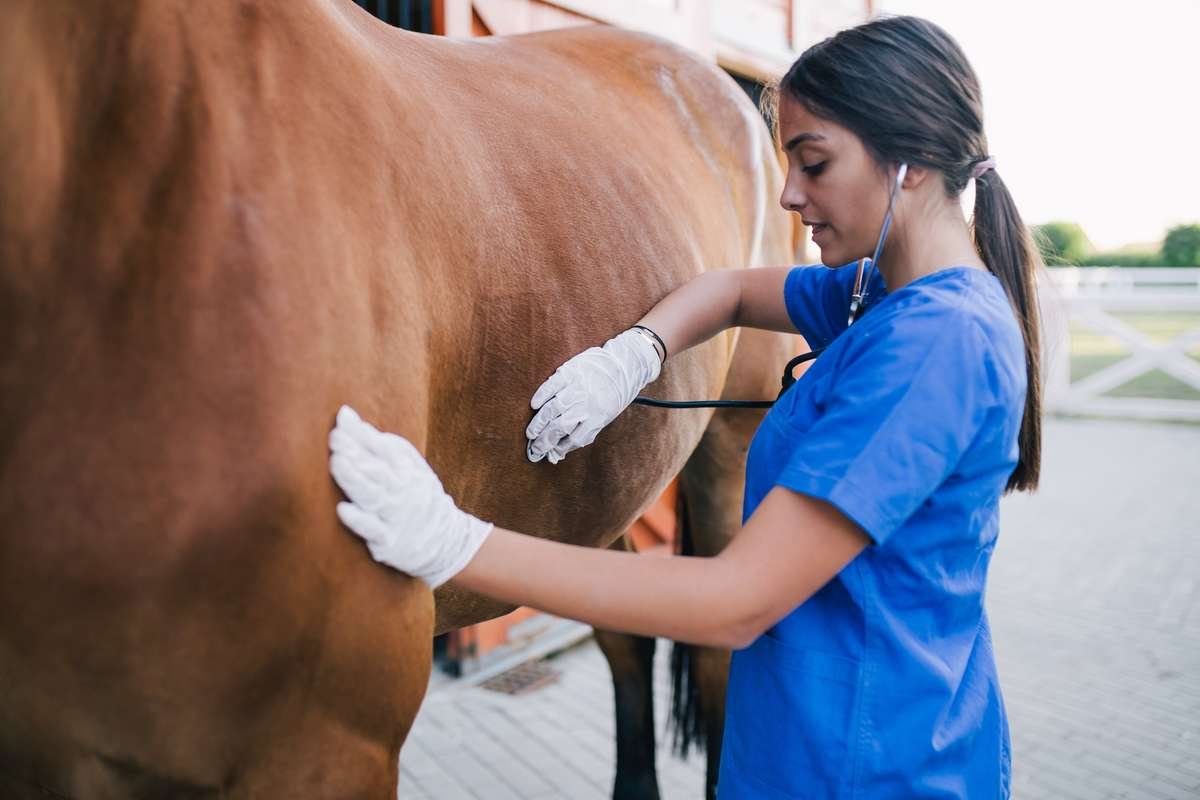

If the cause of respiratory disease cannot be determined after an initial medical history, further diagnostic measures should be initiated.
Blood gas analysis (BGA) – performance test for the lungs
Blood gas analysis is a widely used diagnostic tool to determine the horse's lung capacity and oxygen supply at rest and during exertion. Blood gas analysis can also be used to diagnose heart disease. Arterial blood is taken from the horse for this purpose. The blood taken is analyzed directly in an analysis device.
Then it becomes strenuous for the horse: 10 minutes of trotting and 5 minutes of galloping must be overcome before the next blood sample is taken. For horses with particularly severe respiratory problems, the duration of the exercise can be shortened in consultation with the vet if it becomes too strenuous for the horse. After the exercise, arterial blood is taken again as soon as possible and analyzed again.
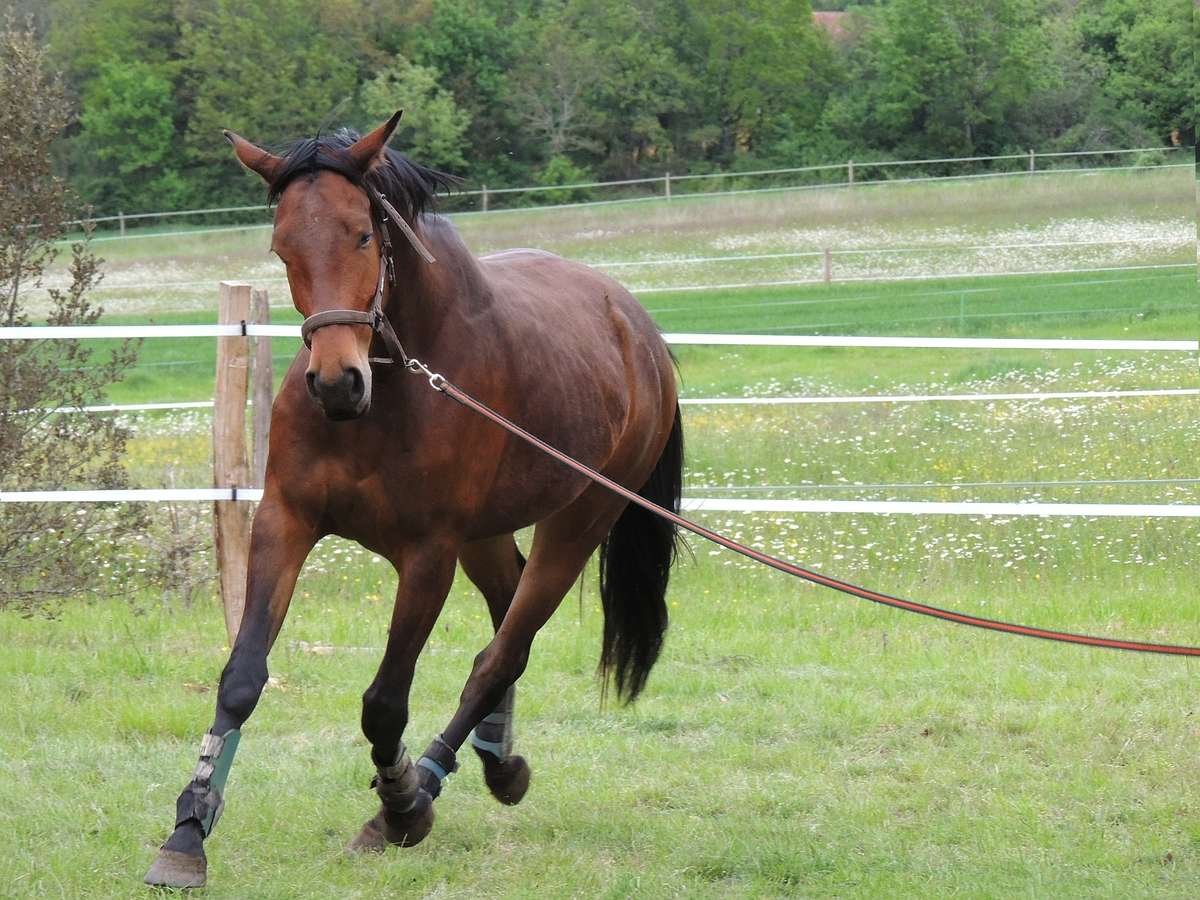

Now it gets strenuous - the horse has to be lunged for the blood gas analysis.
BGA – What is measured and what do the values mean?
When analyzing blood gas values, not only the oxygen level is measured, but a whole series of measurements are taken. For laypeople, these values look more than confusing at first glance. We have broken down what the abbreviations mean and which values are normal.
PH value:
pH value of the blood. If the pH value of the blood is too low, this can indicate acidosis. If the pH value of the blood is too high, this indicates alkalosis.
pH value of the blood. If the pH value of the blood is too low, this can indicate acidosis. If the pH value of the blood is too high, this indicates alkalosis.
PaO2 (partial pressure of oxygen):
Measured value for the proportion of oxygen in the blood. This value is particularly informative about the oxygen exchange in the lungs. If the arterial oxygen partial pressure is too low, this indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood, which is caused by disturbances in the alveolar gas exchange.
Measured value for the proportion of oxygen in the blood. This value is particularly informative about the oxygen exchange in the lungs. If the arterial oxygen partial pressure is too low, this indicates a lack of oxygen in the blood, which is caused by disturbances in the alveolar gas exchange.
PaCO2 (carbon dioxide partial pressure):
Measured value for the proportion of carbon dioxide in the blood. This value is particularly significant for lung ventilation. If the partial pressure of carbon in the blood is too high, this indicates a serious disturbance of gas exchange in the lungs.
Measured value for the proportion of carbon dioxide in the blood. This value is particularly significant for lung ventilation. If the partial pressure of carbon in the blood is too high, this indicates a serious disturbance of gas exchange in the lungs.
HCO3- (blood bicarbonate content):
Measured value for the CO2 binding capacity of the blood. If the bicarbonate content of the blood is too high, this can indicate acidosis. If it is too low, this can indicate alkalosis.
Measured value for the CO2 binding capacity of the blood. If the bicarbonate content of the blood is too high, this can indicate acidosis. If it is too low, this can indicate alkalosis.
Base deviation:
Measure of the acid-base balance of the blood and can be used to estimate the deviation from the normal buffer capacity.
Measure of the acid-base balance of the blood and can be used to estimate the deviation from the normal buffer capacity.
AaPO2 (alveo-arterial oxygen partial pressure difference):
Difference in the partial pressure of oxygen between alveoli and arterial blood. Independent of pressure and temperature like PaO2. An increased value of the alveo-arterial partial pressure difference of oxygen indicates a lung dysfunction.
Difference in the partial pressure of oxygen between alveoli and arterial blood. Independent of pressure and temperature like PaO2. An increased value of the alveo-arterial partial pressure difference of oxygen indicates a lung dysfunction.
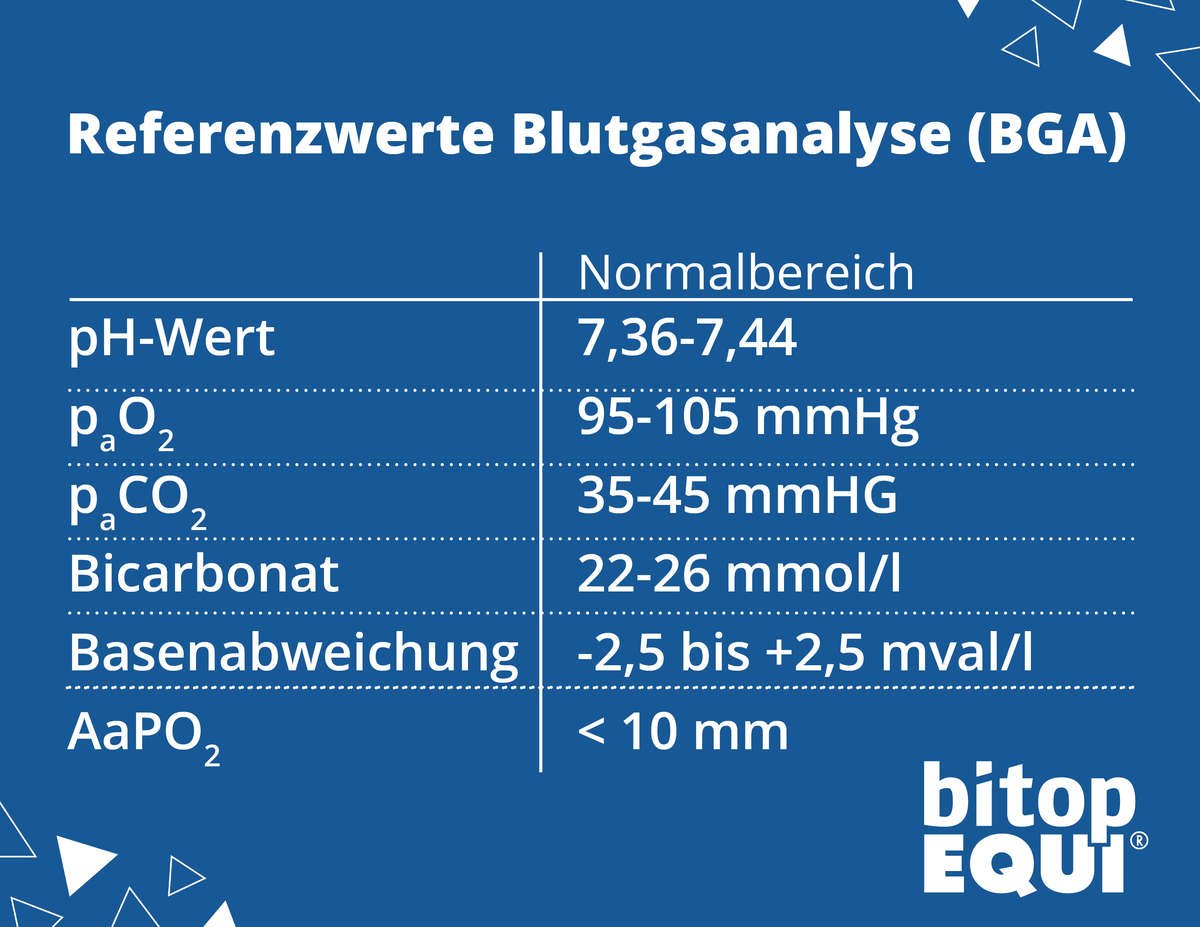
There are reference values for blood gas analysis. Deviations should always be discussed with the veterinarian. (1,2)
Acidosis and alkalosis - when is the blood too acidic?
The pH value, bicarbonate content and alkaline deviation of the blood provide an indication of whether the horse is heading towards alkalosis or acidosis or even already has one. But what do acidosis and alkalosis actually mean? And what do they have to do with breathing? We'll explain it to you:
Respiratory acidosis:
Respiratory acidosis is a condition caused by a gas exchange disorder in horses. The horse can no longer exhale enough CO2, which leads to an accumulation of H+ ions and HCO3- ions in the blood. Chronic acidosis can be almost asymptomatic. However, it is often accompanied by shortness of breath, poor performance and balance problems.
Respiratory alkalosis:
Respiratory alkalosis in horses is caused by excessive exhalation of CO2, as occurs, for example, in hyperventilation. However, this is very rare in horses. However, alkalosis can be very problematic, as the concentration of free cations increases when the blood pH is increased.
reduced - this can cause cardiac arrhythmias or cardiac-synchronous diaphragmatic contractions. Respiratory-related alkalosis does NOT indicate respiratory problems , but occurs in extreme situations such as severe pain or neurological problems.
reduced - this can cause cardiac arrhythmias or cardiac-synchronous diaphragmatic contractions. Respiratory-related alkalosis does NOT indicate respiratory problems , but occurs in extreme situations such as severe pain or neurological problems.
Attention: Acidosis and alkalosis are not always caused by respiratory problems. Other causes (such as heart problems, kidney dysfunction or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract) can also trigger acidosis or alkalosis.
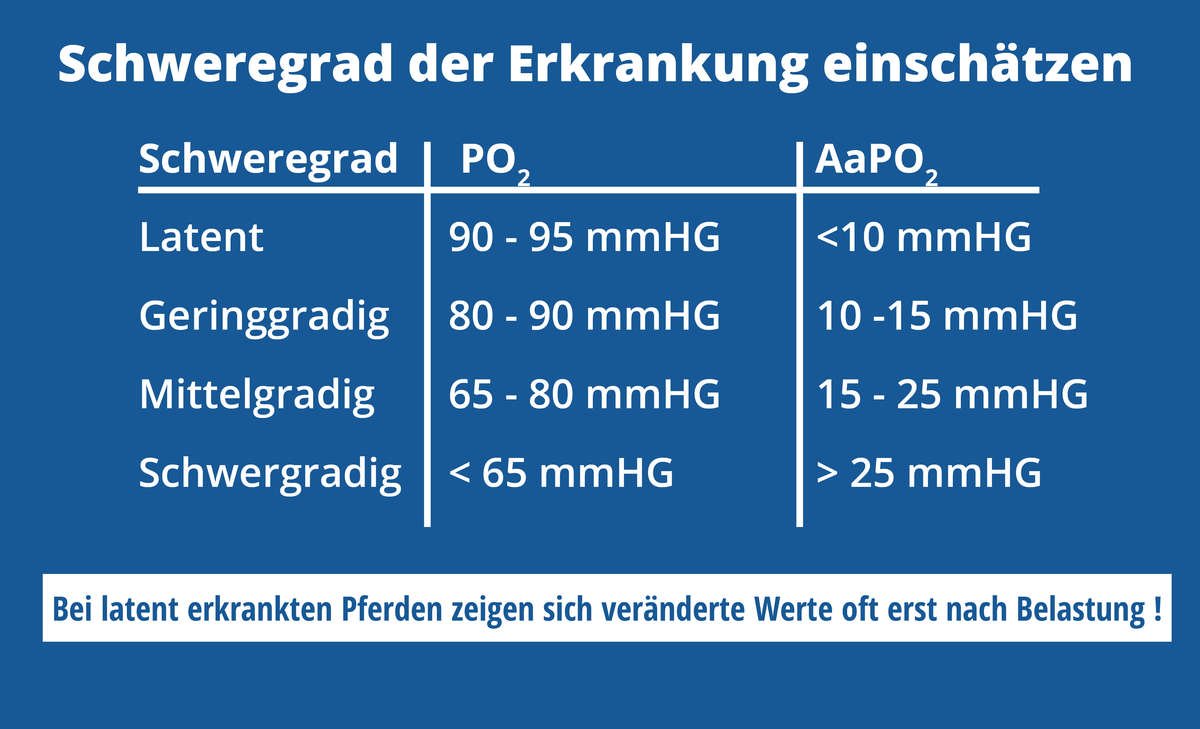
Based on the blood gas analysis values, the veterinarian can make an initial assessment
the severity of a horse's respiratory disease.
the severity of a horse's respiratory disease.
In the table you can see an overview of the severity assessment based on the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) and the alveo-arterial
Oxygen partial pressure difference (AaPO2).
Oxygen partial pressure difference (AaPO2).
It is important to know that in the case of latent respiratory problems due to
the compensatory capacity of the lungs leads to a deterioration of the values
during and after the load. Therefore, it makes sense to have a BGA
both before and after exercise.
the compensatory capacity of the lungs leads to a deterioration of the values
during and after the load. Therefore, it makes sense to have a BGA
both before and after exercise.
Bronchoscopy – a look at the inner values
To get a more precise picture of the condition of the horse's respiratory tract, the veterinarian can order a bronchoscopy. The horse is lightly sedated and then a flexible endoscope is inserted through the nostrils into the upper respiratory tract. With the help of the camera, which is attached to the tip of the endoscope, the veterinarian can view the upper respiratory tract and the trachea up to the division into the main bronchi.
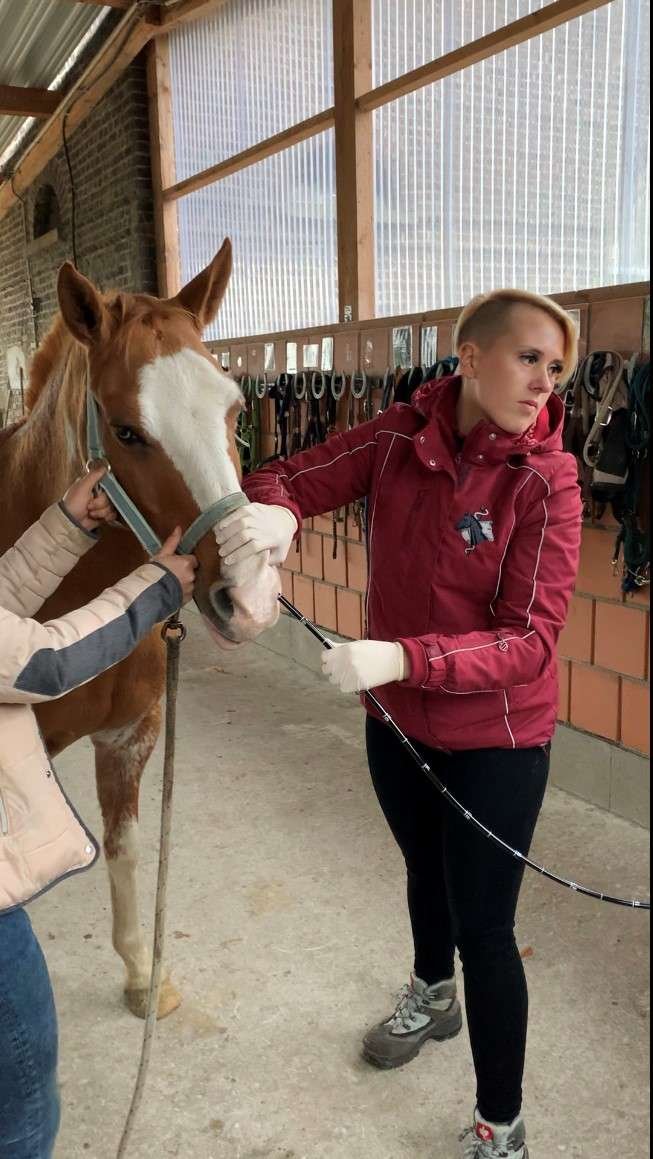

The endoscope is inserted through the nostril
The endoscopy can be followed in real time on the monitor. The doctor can not only see the amount and nature of secretion accumulations , but also assess the presence of mucous membrane changes , such as redness and swelling.
Through the working channel of the endoscope, a
A sample of the mucus deposits is taken. This is then analyzed in the laboratory
cytologically and bacteriologically examined and thus provides important information
on the cause of the respiratory problems.
Through the working channel of the endoscope, a
A sample of the mucus deposits is taken. This is then analyzed in the laboratory
cytologically and bacteriologically examined and thus provides important information
on the cause of the respiratory problems.
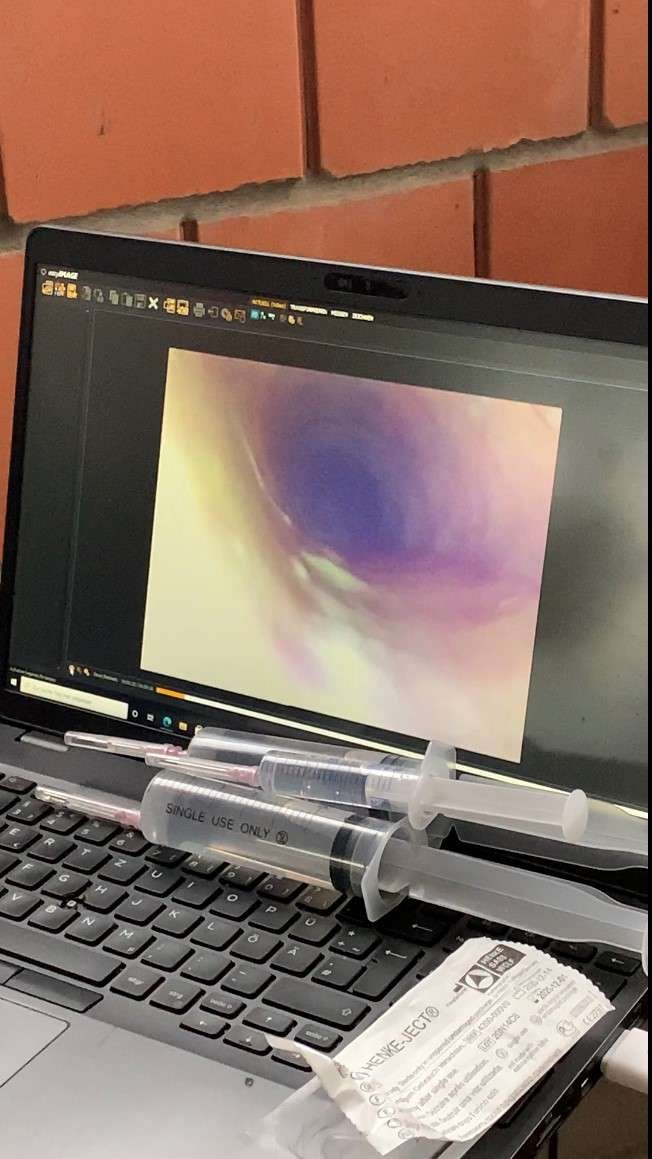
Significant mucus deposits in the respiratory tract indicate a chronic respiratory problem
In special cases or when the amount of secretion in the airways is insufficient, a bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) can be performed. The lungs are flushed with 250–500 ml of saline solution in order to obtain lavage samples for laboratory examination.
Laboratory diagnostics – tracking down the culprit
Samples obtained during bronchoscopy or BAL are examined bacteriologically and cytologically in the laboratory.
This can help narrow down the type and cause of respiratory problems
But what do the abbreviations and numbers on the laboratory report actually mean?
This can help narrow down the type and cause of respiratory problems
But what do the abbreviations and numbers on the laboratory report actually mean?
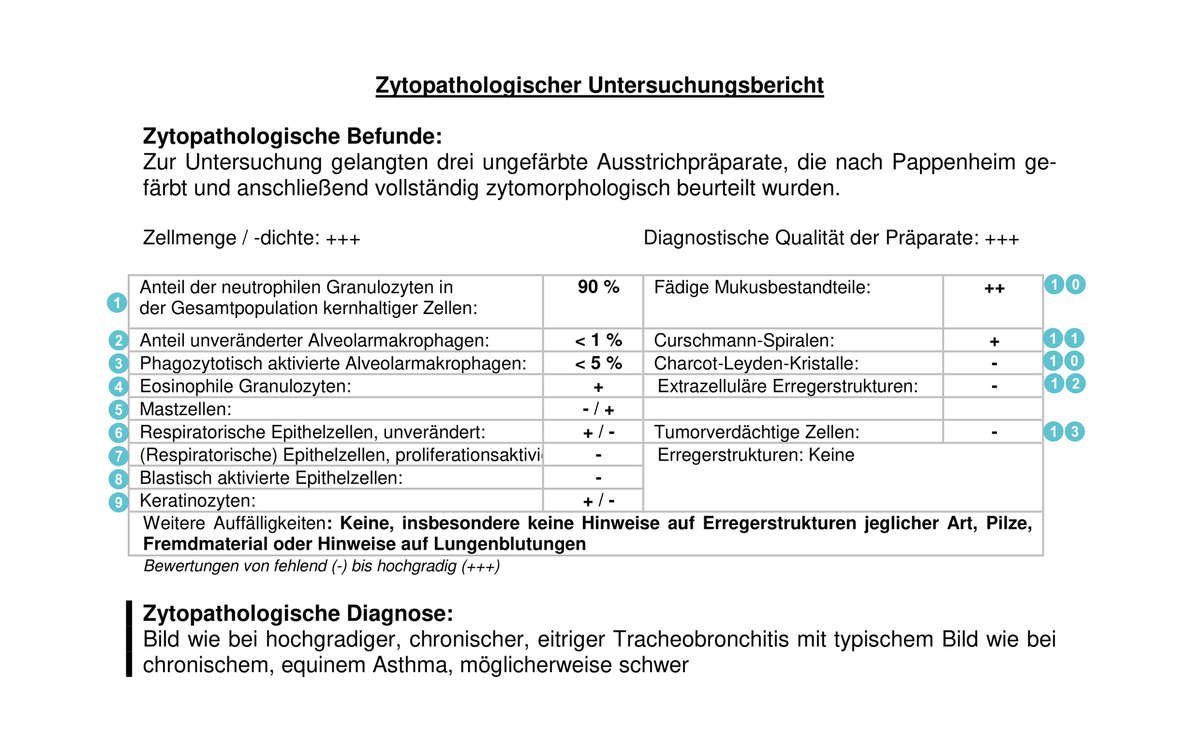
What does what mean?
1. Neutrophil granulocytes: subtype of white blood cells and
Part of the cellular immune system. They are primarily responsible for the initial defense against bacteria. If these occur frequently, this is an indication of inflammatory processes or equine asthma .
Part of the cellular immune system. They are primarily responsible for the initial defense against bacteria. If these occur frequently, this is an indication of inflammatory processes or equine asthma .
2. Alveolar macrophages: phagocytes of the immune system that are responsible, among other things, for cleaning the lungs of foreign particles. Increased values indicate bacterial inflammation or equine asthma . In higher degrees of equine asthma, the proportion of macrophages decreases relative to neutrophil granulocytes.
3. Phagocytotically activated alveolar macrophages: Alveolar macrophages,
who are currently busy absorbing and digesting foreign bodies. Increased values indicate inflammation , but can also indicate an improvement in the lungs' self-cleaning ability after a previous respiratory infection.
who are currently busy absorbing and digesting foreign bodies. Increased values indicate inflammation , but can also indicate an improvement in the lungs' self-cleaning ability after a previous respiratory infection.
4. Eosinophil granulocytes: White blood cells that are responsible for cellular defense, especially against parasites and worms. A strong increase in their number indicates parasite infestation (lungworms) , moderate increases indicate IAR or ROA .
5.Mast cells: Cells of the body's own defense system that store the messenger substances histamine and heparin. They play an important role in the development of allergies. Elevated values therefore indicate allergic asthma .
6. Epithelial cells: Cells of the mucous membrane that lines the respiratory tract. Increased occurrence is often an indication of changes in the mucous membranes due to chronic inflammatory processes. However, squamous epithelial cells in particular can stick to the endoscope when it is inserted - so they do not necessarily indicate a disease of the lower respiratory tract.
7. Proliferation-activated epithelial cells: Epithelial cells that are engaged in division and proliferation.
8. Blastically activated epithelial cells: Young, undifferentiated cells that have not yet divided. Increased occurrence indicates chronic damage to the airways.
9. Keratinocytes: Cells specialized in the production of keratin.
10. Threadlike mucus components: Threadlike and stringy components in the mucus.
11. Curschmann spirals: Mucus spirals that occur in sputum in bronchitis and asthma. Their presence is a characteristic indication of an obstruction of the small airways and a disturbance of the self-cleaning of the bronchi.
12. Charcot-Leyden crystals: Crystalline structures that occur in diseases with a strong eosinophilic component. They indicate allergic bronchitis.
13. Extracellular pathogens: Fungi, bacteria and other pathogens that occur outside the cells. Increased values indicate a reduction in the self-cleaning ability of the lungs and/or poor living conditions . In addition, an increased bacterial content can indicate a bacterial cause .
14. Suspected tumor cells: Cells that show changes that make them suspect for the formation of a tumor. Elevated values are an indication of tumors in the respiratory tract.
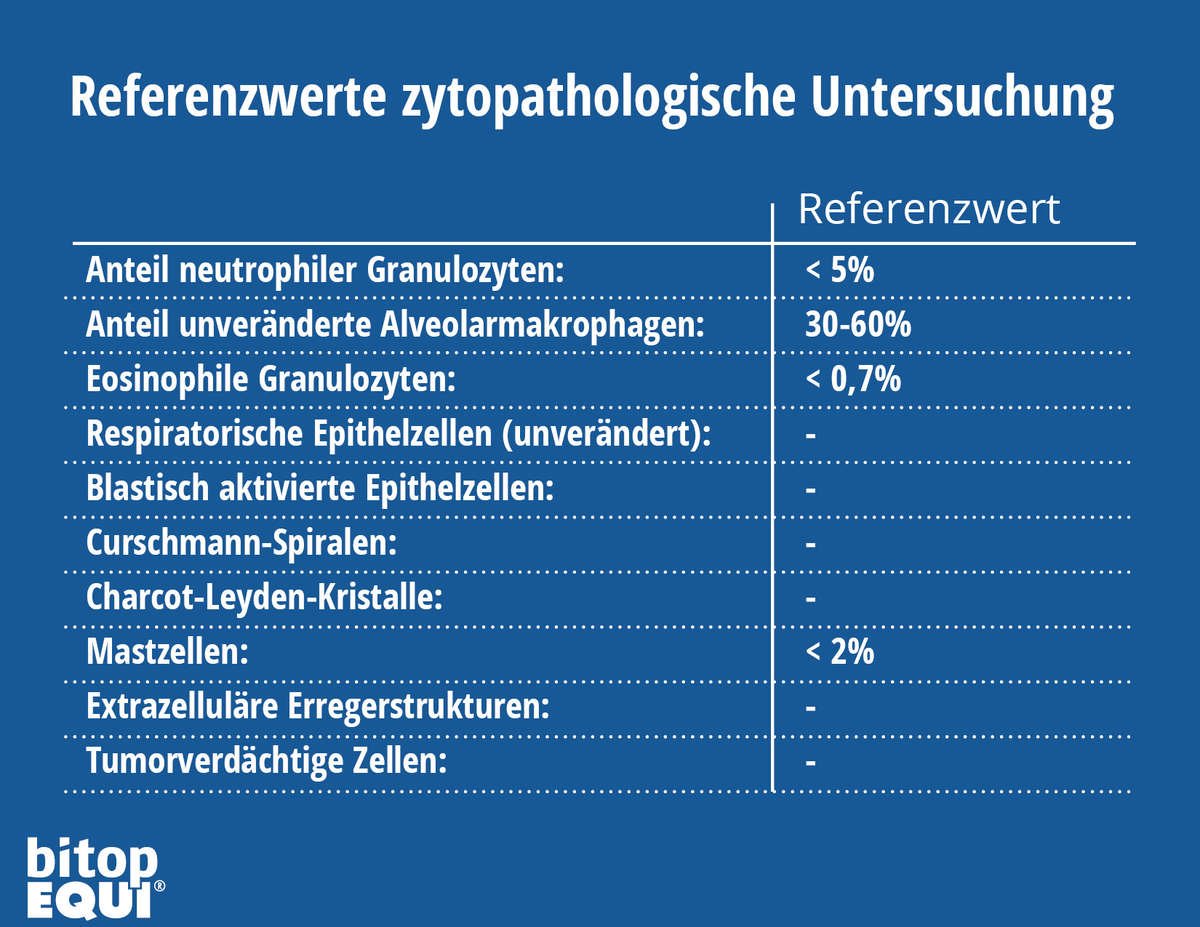
What are the reference values?
In addition to the explanations of the technical terms, it is particularly interesting for horse owners to know which values are physiological, i.e. "normal" for the owner, so that he can assess the condition of his horse. For such an initial assessment, you will find corresponding reference values in the table.
Of course, every laboratory result should be discussed with the veterinarian in order to coordinate any possible therapy for the horse.
Benefits and limitations of bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is one of the most commonly used diagnostic procedures for horses with respiratory diseases. It allows an assessment of the health of the respiratory tract. The veterinarian can check the mucous membranes for redness, swelling or abnormal changes. The amount and quality of bronchial secretions can also be checked. Bronchoscopy also offers the possibility of taking secretion samples, which can be analyzed in the laboratory.
Limitations of bronchoscopy:
Of course, bronchoscopy, like any other diagnostic procedure, has its limitations. These arise in particular from the type of examination: the endoscope can only examine as far as the main bronchi. Changes in the lungs cannot therefore be detected by bronchoscopy.
Further diagnostic measures:
If bronchoscopy and blood gas analysis cannot provide more precise information about the cause of the respiratory problems, the veterinarian can resort to further diagnostic measures. These include:
Limitations of bronchoscopy:
Of course, bronchoscopy, like any other diagnostic procedure, has its limitations. These arise in particular from the type of examination: the endoscope can only examine as far as the main bronchi. Changes in the lungs cannot therefore be detected by bronchoscopy.
Further diagnostic measures:
If bronchoscopy and blood gas analysis cannot provide more precise information about the cause of the respiratory problems, the veterinarian can resort to further diagnostic measures. These include:
- Ultrasound: Using an ultrasound device, the pleura, heart and lung tissue that does not contain air can be examined further. Inflammatory lung changes, abscesses and tumors can be detected if they are on the surface of the lungs, but deeper structures cannot be imaged. In addition, fluid accumulations (for example due to pleural effusion) can be detected.
- X-rays: Since X-rays penetrate tissue containing air well, X-rays are very good for assessing the lungs. Pathological changes such as tumors, abscesses and chronic inflammations can be easily seen on an X-ray. But air or fluid accumulations in the lungs (for example in the case of a pneumothorax, pulmonary hemorrhage or pulmonary edema) can also be easily imaged. X-rays are also used to diagnose pneumonia.
- Lung biopsy: A lung biopsy is performed by the veterinarian primarily when unusual changes in the lung tissue are seen during ultrasound or X-ray. The sample taken is then examined in the laboratory to determine parameters such as inflammation levels or tumor cells.
Sources
1. Brehm, Handbook of Equine Practice
2. Kraft & Dürr, Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics in Veterinary Medicine
2. Kraft & Dürr, Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics in Veterinary Medicine


4 comments
Super, vielen Dank! Das konnte ich jetzt 1:1 mit dem Laborchinesisch abgleichen und habe ein besseres Verständnis.
Vielen Dank für diesen tollen Artikel. Selbst ein Laie versteht ihn und Laborbefunde bekomme einen Sinn.
Hallo, es hat mir geholfen, Werte besser zu verstehen und die Graviditaet einordnen zu können. Das hilft, um zu wissen wie weit ich das Pferd mobilisieren darf.
Ein wirklich toller und für Laien gut verständlicher Beitrag. Hilfreich sind die Tabellen mit den Referenzierten.